Technology is evolving at an unprecedented pace, transforming the way we live, work, and interact. As we step into 2025, emerging trends are reshaping industries and redefining innovation. In this blog post, we explore the top 10 technology trends of 2025, detailing their origins, applications, importance, risks, and how to adopt them.
1. Generative AI

What is Generative AI?
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to AI systems that can generate text, images, music, videos, and even code. These models use deep learning to create realistic and coherent content based on training data.
When Did It Start?
Generative AI gained prominence with the introduction of models like GPT-3 (2020) and DALL·E, but its roots trace back to early AI research in the 1950s.
How to Use It?
- Content creation: Writing blogs, generating social media posts
- Design and art: Creating images, music, and videos
- Software development: Automating coding processes
Importance
- Enhances productivity by automating creative tasks
- Saves costs on hiring designers, writers, and coders
- Provides personalized customer interactions
Side Effects
- Ethical concerns: Deepfake generation and misinformation
- Copyright issues due to AI-generated content
- Potential job displacement in creative industries
How to Adopt It?
Businesses can integrate AI-powered tools such as ChatGPT, Jasper, or MidJourney to enhance workflows and productivity.
The Rise of Generative AI in 2025: Revolutionizing Industries and Transforming Creativity
Introduction
Generative AI has emerged as one of the most transformative technological advancements of our time. From AI-generated text and images to automated content creation, Generative AI in 2025 is revolutionizing industries and reshaping the way businesses operate. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what Generative AI is, its applications, benefits, challenges, and the future trends that will define its growth.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that can create new content, including text, images, videos, code, and even music. Unlike traditional AI models that analyze and predict, Generative AI produces unique and realistic content based on patterns learned from vast datasets.
How Does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI is powered by advanced deep learning models, including:
- Transformers (GPT, Gemini, Claude) – Used for text generation
- Diffusion Models (DALL·E, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion) – Used for image and video generation
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) – Used for realistic image synthesis
- VAEs (Variational Autoencoders) – Used in data augmentation and design automation
Key Applications of Generative AI in 2025
Generative AI is impacting multiple industries, enhancing creativity, efficiency, and automation.
1. Content Creation & Marketing
- AI-generated blog posts, articles, and social media content
- Automated ad copy for digital marketing campaigns
- AI-powered video editing and animation
Example: Companies like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Jasper AI help businesses automate content creation, improving SEO and engagement.
2. Software Development & Code Generation
- AI-assisted programming with tools like GitHub Copilot
- Automated bug detection and debugging
- AI-powered low-code/no-code development
Example: AI-driven platforms allow non-coders to develop applications quickly, making software development more accessible.
3. AI in Healthcare & Drug Discovery
- AI-powered medical imaging and diagnostics
- Personalized medicine through AI-driven genetic analysis
- AI-assisted drug discovery and molecule generation
Example: Generative AI accelerates drug discovery, reducing development time and improving patient outcomes.
4. Gaming & Virtual Reality (VR/AR)
- AI-generated NPCs with human-like interactions
- AI-created game environments and assets
- Personalized AI-powered storylines in gaming
Example: AI is used in game development to create lifelike characters and dynamic virtual worlds.
5. Financial Services & Fraud Detection
- AI-generated financial reports and investment analysis
- AI-powered chatbots for customer service in banking
- AI fraud detection in real-time transactions
Example: Financial institutions use AI to enhance security, predict risks, and optimize trading strategies.
6. E-Commerce & Personalized Shopping
- AI-generated product descriptions and customer reviews
- Personalized AI-driven shopping recommendations
- AI-powered virtual try-ons and augmented shopping experiences
Example: E-commerce giants like Amazon and Shopify leverage AI to enhance user experience and increase conversions.
7. Legal & Compliance Automation
- AI-generated contracts and legal documentation
- AI-powered case law research and analysis
- Compliance monitoring with AI-driven risk assessment
Example: AI in the legal industry speeds up contract review, reducing manual workload for lawyers.
Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI offers numerous advantages, making it an indispensable technology for businesses and individuals alike.
1. Increased Efficiency & Automation
AI-generated content reduces manual labor, allowing businesses to scale operations faster.
2. Cost Reduction
Companies save on content creation, software development, and marketing expenses by utilizing AI automation.
3. Enhanced Creativity
Generative AI serves as a creative partner, assisting writers, designers, and artists in producing high-quality content.
4. Personalization at Scale
AI enables hyper-personalized experiences, from customized content recommendations to individualized shopping experiences.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite its advantages, Generative AI comes with challenges that need to be addressed.
1. Deepfakes & Misinformation
AI-generated deepfakes can be used for spreading misinformation, posing a significant risk to media and politics.
2. Bias & Fairness Issues
AI models can inherit biases from training data, leading to discriminatory content and unfair decision-making.
3. Copyright & Ownership Concerns
Legal questions around AI-generated content ownership remain unresolved, impacting artists, writers, and content creators.
4. AI Regulation & Governance
Governments are introducing AI regulations to ensure transparency, accountability, and ethical AI development.
The Future of Generative AI: What’s Next?
The future of Generative AI is promising, with emerging trends that will shape its next phase of growth.
1. Multimodal AI Models
AI will integrate multiple modalities (text, image, video, and audio) into a single powerful model.
2. AI-Powered Personalized Assistants
AI chatbots will become more context-aware, providing real-time adaptive suggestions tailored to individual needs.
3. Real-Time AI Video & 3D Generation
AI will revolutionize film production, gaming, and metaverse experiences with real-time 3D modeling and AI-generated videos.
4. AI in Smart Cities & Sustainability
AI-powered urban planning will optimize traffic management, energy usage, and public services for smarter cities.
Conclusion
Generative AI in 2025 is transforming industries, driving innovation, and reshaping the future of work. While it presents exciting opportunities, it also demands ethical considerations, regulations, and responsible AI development.
What’s Next?
Are you ready to leverage Generative AI for your business? Stay ahead of the curve by adopting AI-driven tools, exploring AI-powered solutions, and preparing for the AI-driven future.
Share your thoughts! How do you see Generative AI impacting your industry? Let us know in the comments below!
2. Quantum Computing
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing leverages quantum mechanics to perform computations far beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
When Did It Start?
Concepts of quantum computing emerged in the 1980s, but significant breakthroughs came with Google’s quantum supremacy experiment in 2019.
How to Use It?
- Cryptography: Secure communications
- Drug discovery: Simulating molecular structures
- Optimization: Solving complex logistical problems
Importance
- Enables ultra-fast data processing
- Helps in solving problems intractable for classical computers
- Advances medical and material sciences
Side Effects
- High development and operational costs
- Risk of breaking encryption protocols
- Limited accessibility
How to Adopt It?
Companies can partner with IBM Quantum, Google Quantum AI, or D-Wave to explore quantum applications.
The Quantum Computing Revolution in 2025: Transforming Industries and Unlocking New Possibilities
Introduction
Quantum computing is rapidly advancing in 2025, marking a new era in computational power. Unlike classical computers, quantum computers leverage quantum mechanics to solve complex problems exponentially faster. This breakthrough technology is set to revolutionize fields such as cryptography, healthcare, artificial intelligence, and material science. In this blog, we’ll explore what quantum computing is, its applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends that will shape the next decade.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a field of computing that utilizes quantum bits (qubits) instead of traditional binary bits (0s and 1s). These qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to superposition and interact through quantum entanglement, allowing for unprecedented computational power.
Key Quantum Computing Concepts:
- Superposition: Qubits can exist in multiple states at once, enabling parallel computations.
- Entanglement: Qubits are interconnected, allowing instant correlation over vast distances.
- Quantum Interference: Helps optimize computations by reinforcing correct solutions and canceling incorrect ones.
Key Applications of Quantum Computing in 2025
Quantum computing is disrupting industries by solving previously unsolvable problems. Here are some of its major applications:
1. Cybersecurity & Quantum Cryptography
- Quantum encryption methods provide ultra-secure communications resistant to hacking.
- Post-quantum cryptography is being developed to protect against quantum attacks.
Example: Companies like IBM and Google are developing quantum-safe encryption standards to safeguard sensitive data.
2. Drug Discovery & Healthcare
- AI-powered quantum simulations accelerate the discovery of new drugs and molecules.
- Quantum models help analyze complex biological interactions for personalized medicine.
Example: Pharmaceutical companies use quantum-powered drug modeling to reduce time and cost in developing new treatments.
3. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
- Quantum algorithms enhance machine learning by optimizing data analysis and pattern recognition.
- AI models trained on quantum computers outperform classical AI systems in predictive analytics.
Example: Google’s Quantum AI division is improving AI model efficiency using quantum-enhanced computations.
4. Financial Modeling & Risk Analysis
- Quantum computing helps optimize financial portfolios, fraud detection, and risk management.
- Real-time simulations provide faster, more accurate financial predictions.
Example: Banks and financial institutions are leveraging quantum computing for high-speed risk assessments and trading algorithms.
5. Climate Modeling & Sustainability
- Quantum computers can simulate climate patterns with higher accuracy.
- Helps in optimizing energy use and developing sustainable materials.
Example: Researchers use quantum models to design efficient solar panels and carbon capture technologies.
6. Supply Chain & Logistics Optimization
- Quantum algorithms improve route optimization, demand forecasting, and logistics planning.
- AI-powered quantum solutions reduce costs and increase efficiency.
Example: Companies like DHL and FedEx are integrating quantum computing into their logistics networks for better delivery efficiency.
7. Aerospace & Defense
- Quantum simulations assist in the design and testing of aircraft and defense systems.
- Quantum sensors improve radar detection and secure communication networks.
Example: NASA is using quantum computing for space mission simulations and navigation.
Benefits of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing offers game-changing advantages that classical computers cannot match:
1. Exponential Processing Power
Quantum computers perform calculations in seconds that would take traditional supercomputers millennia.
2. Breakthroughs in Problem-Solving
Quantum computing enables solutions to problems previously deemed computationally impossible.
3. Advancements in AI and Big Data
Quantum AI accelerates deep learning and machine learning for faster, more accurate predictions.
4. Enhanced Cybersecurity
Quantum encryption ensures ultra-secure communications, protecting against cyber threats.
Challenges & Ethical Concerns in Quantum Computing
Despite its potential, quantum computing faces significant challenges:
1. Hardware Limitations & Stability
- Qubits are extremely fragile and require near absolute zero temperatures.
- Quantum decoherence causes errors in calculations, making stability a challenge.
2. High Costs & Infrastructure Requirements
- Quantum computing research requires significant investment in specialized hardware.
- Maintaining quantum systems is expensive and energy-intensive.
3. Security Threats & Cryptography Risks
- Quantum computers could break existing encryption protocols, requiring new quantum-safe cryptography.
- Cybersecurity experts must develop quantum-resistant security systems before large-scale deployment.
4. Accessibility & Skill Gaps
- There is a shortage of quantum computing professionals.
- Governments and institutions must train the next generation of quantum engineers.
The Future of Quantum Computing: What’s Next?
Quantum computing is progressing rapidly, with several exciting trends emerging:
1. Quantum Cloud Computing
- Companies like IBM, Google, and Amazon are offering quantum cloud services, making quantum computing accessible to businesses.
2. Hybrid Quantum-Classical Computing
- Researchers are developing hybrid systems where quantum and classical computers work together for optimized problem-solving.
3. Advancements in Quantum Hardware
- Innovations in topological qubits and superconducting circuits will enhance quantum computer stability and efficiency.
4. Quantum AI & Machine Learning Synergy
- Quantum-enhanced AI models will redefine big data processing, pattern recognition, and natural language processing.
5. Global Quantum Computing Race
- Countries like China, the US, and Europe are heavily investing in quantum research, competing to achieve quantum supremacy.
Conclusion
Quantum computing is ushering in a new era of scientific breakthroughs, AI advancements, and cybersecurity transformations. While challenges remain, the potential impact on medicine, finance, AI, and climate science is undeniable.
What’s Next?
Are you ready to explore the potential of quantum computing? Stay ahead by following quantum advancements, investing in quantum education, and preparing for the quantum-driven future.
Share your thoughts! How do you think Quantum Computing will impact your industry? Let us know in the comments below!
3. 5G Expansion

What is 5G?
5G is the next-generation wireless technology offering ultra-fast speeds and low latency.
When Did It Start?
Initial 5G deployments began in 2019, and by 2025, global adoption is widespread.
How to Use It?
- Enhanced mobile broadband
- Smart cities and IoT devices
- Cloud gaming and AR/VR applications
Importance
- Faster internet speeds
- Supports IoT and autonomous vehicles
- Enables real-time connectivity
Side Effects
- High infrastructure costs
- Health concerns (though unproven)
- Increased cybersecurity threats
How to Adopt It?
Telecom providers and enterprises should upgrade network infrastructure and invest in 5G-compatible devices.
The Expansion of 5G in 2025: Transforming Connectivity and Enabling the Future
Introduction
The global rollout of 5G technology in 2025 is revolutionizing industries and enhancing connectivity across the world. With ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and improved network reliability, 5G expansion is accelerating advancements in IoT, smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and remote work. This blog explores what 5G is, its key applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends that will define its growth.
What is 5G?
5G is the fifth-generation mobile network that offers faster data transmission, reduced latency, and increased network capacity compared to its predecessor, 4G LTE. It leverages millimeter waves (mmWave), small cells, and beamforming to improve performance and connectivity.
Key Features of 5G:
- High Speed: Up to 10 Gbps, significantly faster than 4G.
- Ultra-Low Latency: Less than 1 millisecond, crucial for real-time applications.
- Massive Connectivity: Supports up to 1 million devices per square kilometer.
- Energy Efficiency: More efficient than previous networks, reducing power consumption.
Key Applications of 5G in 2025
5G technology is transforming multiple sectors, enabling faster communication, automation, and innovation.
1. Internet of Things (IoT) & Smart Cities
- 5G-enabled smart cities improve traffic management, waste disposal, and energy efficiency.
- IoT devices such as smart meters, sensors, and AI-powered surveillance rely on 5G for real-time data exchange.
Example: Cities like Singapore and Dubai are leveraging 5G-powered IoT to enhance public services and infrastructure.
2. Autonomous Vehicles & Smart Transportation
- 5G allows instant vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication.
- Enables self-driving cars to make real-time decisions based on road conditions and traffic flow.
Example: Companies like Tesla and Waymo use 5G to enhance autonomous driving capabilities.
3. Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR)
- 5G-powered AR/VR experiences enable immersive gaming, training, and education.
- Businesses use AR for interactive marketing and remote collaboration.
Example: 5G enhances metaverse experiences by providing low-latency, high-bandwidth connections.
4. Remote Work & Telecommunication
- 5G improves video conferencing, cloud computing, and virtual collaboration tools.
- Companies can implement 5G private networks for secure and high-speed data access.
Example: Enterprises use 5G-powered hybrid work models to improve productivity and remote access.
5. Healthcare & Telemedicine
- 5G enables real-time remote surgeries and AI-powered diagnostics.
- High-speed data transfer improves medical imaging and remote patient monitoring.
Example: Hospitals are using 5G robots and AI-driven healthcare applications to enhance patient care.
6. Industrial Automation & Smart Factories
- 5G enhances real-time monitoring of industrial machinery for predictive maintenance.
- AI-powered robotics and automation improve manufacturing efficiency.
Example: Companies like Siemens and Bosch use 5G-enabled automation to optimize supply chains.
7. 5G in Entertainment & Media
- Faster streaming and high-resolution gaming with reduced lag.
- AI-driven personalized content recommendations based on real-time data analysis.
Example: Streaming platforms like Netflix and Twitch benefit from 5G’s high-speed and low latency.
Benefits of 5G Expansion
The widespread adoption of 5G provides numerous advantages:
1. Faster & Reliable Connectivity
5G ensures high-speed internet access with improved network reliability.
2. Reduced Network Congestion
Supports millions of devices simultaneously without slowdowns.
3. Improved Remote Work & Digital Inclusion
Expands internet access to rural areas, bridging the digital divide.
4. Revolutionizing Smart Cities & IoT
Drives sustainable urban development through AI-powered infrastructure.
5. Economic Growth & Job Creation
5G fuels technological innovation, startup growth, and job opportunities.
Challenges & Concerns of 5G Expansion
Despite its potential, 5G faces technical, regulatory, and security challenges:
1. Infrastructure Costs & Deployment Challenges
- 5G requires new base stations, fiber optic networks, and small cell towers.
- Rural and developing regions face slower adoption due to high costs.
2. Security & Privacy Risks
- 5G networks increase cybersecurity risks due to higher connectivity.
- AI-driven cyberattacks and data breaches require advanced security protocols.
3. Health & Environmental Concerns
- Some concerns exist about radiation exposure from 5G towers.
- Studies are ongoing to assess long-term health and environmental impacts.
4. Global 5G Competition & Geopolitical Conflicts
- Countries like China, the US, and Europe are competing for 5G dominance.
- Trade restrictions and regulations impact 5G equipment supply chains.
Future of 5G: What’s Next?
The evolution of 5G will drive new innovations in connectivity and digital transformation.
1. 5G-Advanced (5G-A) & 6G Development
- 5G-A will enhance AI-driven automation, latency reduction, and bandwidth efficiency.
- 6G research is underway, focusing on AI-powered networking and terahertz frequencies.
2. AI & Edge Computing Integration
- AI-powered network optimization will enhance 5G performance and security.
- Edge computing + 5G will reduce latency in IoT and industrial applications.
3. Satellite-5G Hybrid Networks
- Integration of satellite-based 5G networks for global high-speed coverage.
- Companies like SpaceX’s Starlink and Amazon’s Project Kuiper are working on 5G-compatible satellite services.
4. Increased 5G Accessibility & Smart Cities Expansion
- Governments and telecom providers are expanding 5G infrastructure to underserved areas.
- More smart city projects will rely on 5G for AI-powered urban planning.
Conclusion
The expansion of 5G in 2025 is revolutionizing industries, enabling real-time applications, and driving digital transformation. While challenges remain, the future of 5G promises enhanced connectivity, AI-driven automation, and global economic growth.
What’s Next?
Are you ready for the 5G revolution? Stay informed about 5G advancements, smart city innovations, and next-gen connectivity solutions.
Share your thoughts! How do you think 5G will impact your business or daily life? Let us know in the comments below!
4. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)

What is VR/AR?
VR immerses users in a simulated environment, while AR overlays digital elements onto the real world.
When Did It Start?
VR dates back to the 1960s, but modern applications gained traction in the 2010s with Oculus and Microsoft HoloLens.
How to Use It?
- Gaming and entertainment
- Training simulations for healthcare and aviation
- Retail and virtual showrooms
Importance
- Enhances training and education
- Creates immersive user experiences
- Drives innovation in multiple industries
Side Effects
- Expensive hardware requirements
- Motion sickness in some users
- Privacy concerns with data tracking
How to Adopt It?
Businesses can develop VR/AR experiences using platforms like Meta’s Horizon Workrooms and Google ARCore.
The Evolution of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in 2025: Reshaping Digital Experiences
Introduction
In 2025, Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are more immersive, interactive, and widespread than ever. These technologies are transforming gaming, education, healthcare, retail, and remote collaboration, enhancing how users engage with digital and physical environments. This blog explores how VR and AR are evolving, their applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
What Are VR and AR?
- Virtual Reality (VR): A fully immersive experience where users interact with a simulated environment via VR headsets.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Enhances the real world by overlaying digital elements onto physical surroundings using AR glasses, smartphones, or headsets.
- Mixed Reality (MR): A blend of VR and AR where users interact with both virtual and real-world objects seamlessly.
Key Applications of VR & AR in 2025
1. Gaming & Entertainment
- Fully immersive VR games with real-time physics and AI-powered NPCs.
- AR-enhanced mobile games that blend digital elements into real-world environments.
- AI-driven VR storytelling and interactive metaverse experiences.
Example: Meta’s Quest 3 and Apple Vision Pro push immersive gaming boundaries, offering haptic feedback and real-world object tracking.
2. Healthcare & Medical Training
- VR-powered surgeries allow doctors to practice complex procedures safely.
- AR aids in real-time diagnostics and remote consultations.
- Mental health therapy uses VR exposure therapy for PTSD and anxiety treatments.
Example: Hospitals integrate AR for 3D visualization of patient anatomy to enhance diagnosis and treatment.
3. Education & Workforce Training
- VR classrooms offer virtual field trips and hands-on simulations.
- AR enhances STEM education by bringing historical figures, scientific concepts, and real-world simulations into lessons.
- Enterprise VR training programs for onboarding, safety procedures, and skill-building.
Example: Schools and universities leverage AI-powered VR learning experiences, making education more engaging and effective.
4. Retail & E-Commerce
- AR-powered virtual try-ons for clothing, accessories, and makeup.
- VR showrooms allow customers to explore products in a 3D virtual space.
- AI-driven personalized shopping experiences using AR recommendations.
Example: Brands like IKEA and Nike use AR for virtual furniture placement and interactive product testing.
5. Remote Work & Collaboration
- VR-based virtual offices and meetings enhance remote teamwork.
- AR-powered holographic presentations and real-time collaboration tools.
- AI-driven VR workspaces improve productivity and engagement.
Example: Companies like Microsoft and Meta develop VR-powered virtual offices for hybrid work solutions.
6. Real Estate & Architecture
- VR house tours let buyers explore properties remotely.
- AR enables real-time 3D architectural visualization for construction planning.
- AI-driven VR simulations allow urban planners to design smart cities.
Example: Architects use VR modeling tools for client presentations and building previews.
7. Automotive & Manufacturing
- VR-based design and prototyping accelerate product development.
- AR-powered assembly line training and real-time maintenance assistance.
- AI-driven VR crash testing and vehicle simulations.
Example: Automakers like Tesla and BMW use VR for vehicle design and testing before production.
Benefits of VR & AR
1. Enhanced User Engagement
Immersive experiences increase learning retention, productivity, and user satisfaction.
2. Real-Time Data Integration
AR enables instant access to real-time data, improving decision-making in healthcare, business, and logistics.
3. Cost-Effective Training & Development
VR reduces training costs by offering realistic simulations without the need for physical materials.
4. Improved Accessibility & Inclusivity
AR/VR enhances accessibility for individuals with disabilities, enabling inclusive experiences in education, work, and entertainment.
Challenges of VR & AR in 2025
1. High Hardware Costs & Adoption Barriers
- VR headsets and AR glasses remain expensive for mainstream adoption.
- Businesses require significant investment in infrastructure and software.
2. Privacy & Security Risks
- Real-time data collection in AR/VR environments raises concerns about data privacy and security.
- AI-driven personalization may increase risks of user profiling and surveillance.
3. Motion Sickness & Health Concerns
- VR experiences may cause motion sickness and eye strain.
- Long-term exposure may impact vision and cognitive function.
4. Content & Software Limitations
- Limited high-quality AR/VR content affects user adoption.
- Developers need more intuitive creation tools to expand VR/AR ecosystems.
Future Trends in VR & AR (2025 & Beyond)
1. AI-Powered VR & AR Experiences
- AI-driven realistic avatars, NPCs, and virtual assistants.
- AI-powered voice recognition for seamless interaction.
2. VR & AR in the Metaverse
- Virtual spaces will replace traditional social media, fostering fully immersive online communities.
- 3D digital twins of real-world locations for virtual tourism and events.
3. Wearable AR Devices & Smart Glasses
- AR smart glasses with AI-powered real-time translation and data overlays.
- Lightweight, wireless VR headsets with 8K resolution and eye tracking.
4. 6G & Edge Computing Enhancements
- Ultra-fast connectivity will reduce VR/AR latency for seamless streaming.
- Edge computing will enable cloud-based AR experiences without bulky hardware.
5. Haptic Feedback & Full-Body VR
- Advanced haptic suits and gloves for realistic VR interactions.
- Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) to enable thought-controlled VR experiences.
Conclusion
VR and AR in 2025 are transforming industries, creating new digital realities and immersive experiences. While challenges remain, continued advancements in AI, connectivity, and hardware will drive broader adoption.
What’s Next?
Are you ready to explore the future of VR and AR? Stay informed about cutting-edge innovations, emerging trends, and industry disruptions.
Share your thoughts! How do you see VR and AR shaping your industry or lifestyle? Let us know in the comments below!
5. Internet of Things (IoT)

What is IoT?
IoT connects everyday devices to the internet, allowing them to communicate and automate tasks.
When Did It Start?
The concept emerged in the 1990s, and smart home devices gained popularity in the 2010s.
How to Use It?
- Smart home devices
- Industrial automation
- Healthcare monitoring
Importance
- Increases efficiency
- Reduces costs through automation
- Enhances data-driven decision-making
Side Effects
- Security vulnerabilities
- Privacy concerns
- High initial investment
How to Adopt It?
Businesses should invest in IoT-compatible devices and enhance cybersecurity protocols.
The Future of the Internet of Things (IoT) in 2025: Transforming Smart Cities, Industries, and Everyday Life
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to revolutionize industries and daily life in 2025, connecting billions of devices worldwide. With advancements in AI, 5G, and edge computing, IoT is driving smarter cities, efficient industries, and personalized consumer experiences. This blog explores key applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends shaping IoT in 2025 and beyond.
What is IoT?
IoT refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data in real-time. These devices range from smart home gadgets to industrial sensors, creating seamless automation and data-driven decision-making.
Key Components of IoT:
- Sensors & Devices: Collect data from the environment.
- Connectivity: 5G, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and LPWAN power IoT communication.
- Edge Computing: Processes data closer to the source, reducing latency.
- AI & Machine Learning: Enhances automation and predictive analytics.
Key Applications of IoT in 2025
1. Smart Cities & Urban Development
- AI-driven traffic management and smart street lighting optimize energy use.
- Real-time air quality monitoring improves public health.
- 5G-powered autonomous public transportation enhances mobility.
Example: Cities like Singapore and Amsterdam use IoT-powered smart grids to optimize energy consumption.
2. Industrial IoT (IIoT) & Manufacturing
- Predictive maintenance reduces downtime and repair costs.
- IoT-driven robotics improve automation in manufacturing.
- AI-powered quality control systems enhance production efficiency.
Example: Companies like Siemens and General Electric implement AI-driven IoT solutions for efficient supply chain management.
3. Healthcare & Remote Patient Monitoring
- Wearable IoT devices track vital signs in real-time.
- AI-powered diagnostics improve early disease detection.
- IoT-enabled telemedicine expands healthcare accessibility.
Example: Hospitals use IoT-connected devices for real-time patient monitoring and smart medical alerts.
4. Smart Homes & Consumer IoT
- AI-driven home automation systems optimize energy use.
- Voice-controlled IoT assistants provide seamless control.
- Smart security cameras enhance home safety.
Example: Devices like Amazon Alexa and Google Nest integrate AI for personalized smart home experiences.
5. Agriculture & Smart Farming
- IoT-based irrigation systems optimize water usage.
- AI-powered drones monitor crop health.
- Connected livestock tracking enhances farm productivity.
Example: Farmers use AI-driven IoT sensors to optimize crop yield and soil health monitoring.
6. Retail & E-Commerce
- IoT-powered smart shelves track inventory in real-time.
- AI-driven personalized shopping experiences improve customer satisfaction.
- Automated checkout systems reduce wait times.
Example: Amazon Go stores use IoT-powered checkout-free shopping to enhance retail experiences.
7. Energy Management & Sustainability
- Smart grids optimize electricity distribution.
- IoT-driven renewable energy systems improve efficiency.
- AI-powered waste management systems reduce environmental impact.
Example: Cities integrate IoT-driven smart meters to monitor and reduce energy consumption.
Benefits of IoT Expansion
1. Improved Efficiency & Automation
IoT reduces manual processes, increasing operational efficiency across industries.
2. Real-Time Data Insights
AI-driven IoT analytics enhance decision-making and predictive maintenance.
3. Cost Savings & Resource Optimization
Smart automation lowers costs by optimizing energy use, inventory management, and maintenance.
4. Enhanced Security & Safety
IoT-powered security systems improve cybersecurity and surveillance in smart cities and industries.
5. Sustainability & Environmental Benefits
IoT reduces waste, optimizes energy consumption, and enhances green technology adoption.
Challenges of IoT Adoption
1. Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Risks
- IoT devices are vulnerable to hacking and cyberattacks.
- Stronger encryption and AI-powered security protocols are needed.
2. High Infrastructure Costs
- Upgrading networks and integrating IoT devices require significant investment.
- Smaller businesses may struggle with affordability.
3. Interoperability & Standardization Issues
- Different manufacturers use varied communication protocols.
- Lack of global IoT standards hinders seamless integration.
4. Scalability & Network Congestion
- Billions of IoT devices strain network bandwidth.
- 5G and edge computing are critical for scalability.
Future Trends in IoT (2025 & Beyond)
1. AI-Driven IoT (AIoT)
- AI-powered predictive analytics enhance automation and decision-making.
- AI-driven IoT chatbots and virtual assistants improve user interactions.
2. 5G-Powered IoT Expansion
- Ultra-low latency 5G networks enhance IoT performance.
- Real-time data processing improves autonomous vehicles, healthcare, and smart cities.
3. Edge Computing & IoT
- Reduces cloud dependency by processing data closer to the source.
- Enhances real-time analytics and cybersecurity.
4. Blockchain for IoT Security
- Ensures secure and transparent IoT transactions.
- Protects IoT networks from cyber threats and data breaches.
5. IoT-Powered Digital Twins
- Virtual models of factories, cities, and supply chains improve efficiency.
- AI-driven real-time monitoring and simulation for predictive maintenance.
6. Sustainable & Green IoT
- IoT innovations optimize renewable energy production and carbon footprint reduction.
- AI-driven climate monitoring systems help combat global warming.
Conclusion
IoT in 2025 is transforming smart cities, industries, healthcare, and everyday life, unlocking unparalleled efficiency and innovation. As IoT adoption grows, advancements in AI, 5G, edge computing, and cybersecurity will drive the next wave of connected intelligence.
What’s Next?
Are you ready to explore the future of IoT and smart automation? Stay informed about IoT trends, AI-driven innovations, and cutting-edge connectivity solutions.
Share your thoughts! How do you see IoT shaping your industry or lifestyle? Let us know in the comments below!
6. Biotechnology in Agriculture

What is Biotech in Agriculture?
Using genetic engineering and biological advancements to enhance crop yield and resilience.
When Did It Start?
Biotech crops were introduced in 1996, and advancements continue today.
How to Use It?
- Genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
- Precision farming
- Sustainable agriculture
Importance
- Improves food security
- Reduces pesticide use
- Enhances climate resilience
Side Effects
- Ethical concerns
- Potential environmental impact
How to Adopt It?
Farmers should collaborate with biotech firms and adopt precision agriculture tools.
The Future of Biotechnology in Agriculture (2025): Advancing Sustainability & Food Security
Introduction
Biotechnology is transforming agriculture in 2025, offering sustainable solutions to global food security, climate resilience, and crop productivity. With advancements in genetic engineering, AI-powered precision farming, and lab-grown foods, biotechnology is helping farmers combat climate change, reduce chemical usage, and optimize yields. This blog explores key applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends shaping biotech in agriculture.
What is Agricultural Biotechnology?
Agricultural biotechnology refers to scientific innovations that enhance crop yield, pest resistance, and soil health using genetic modification, microbiology, and AI-driven analytics.
Key Biotech Innovations in Agriculture:
- Genetically Modified Crops (GMOs): Enhanced resistance to pests, diseases, and extreme weather.
- CRISPR Gene Editing: Precision modifications for drought-resistant and nutrient-rich crops.
- Microbial Soil Enhancements: Biofertilizers and biofungicides replacing chemical-based agriculture.
- AI & Data-Driven Farming: AI-powered predictive analytics for precision agriculture.
- Cellular Agriculture & Lab-Grown Foods: Production of alternative proteins and sustainable food sources.
Key Applications of Biotechnology in Agriculture (2025)
1. Genetically Engineered Crops (GMO & CRISPR) for Climate Resilience
- Drought-resistant corn, rice, and wheat increase crop stability.
- CRISPR-edited crops provide higher nutritional value (e.g., vitamin-rich rice, protein-enhanced wheat).
- Pest and disease-resistant crops reduce reliance on harmful pesticides.
Example: Researchers develop heat-tolerant wheat strains to counteract rising global temperatures.
2. Precision Agriculture with AI & IoT
- AI-powered drones monitor soil health, crop growth, and pest infestations in real time.
- IoT-enabled smart irrigation optimizes water distribution, reducing waste.
- Big data analytics predicts optimal planting times, enhancing productivity.
Example: Farmers use AI-driven sensors to improve soil fertility and maximize crop output.
3. Sustainable Biofertilizers & Biopesticides
- Microbial biofertilizers improve soil health and reduce chemical runoff.
- Natural biopesticides derived from bacteria and fungi replace synthetic pesticides.
- Nitrogen-fixing microbes enhance soil fertility without excessive fertilizers.
Example: Companies like Pivot Bio develop microbial fertilizers to reduce reliance on synthetic nitrogen-based fertilizers.
4. Alternative Proteins & Lab-Grown Food
- Lab-grown meat & plant-based proteins reduce environmental impact.
- Precision fermentation produces dairy-free milk and cheese alternatives.
- Insect-based protein farming provides high-efficiency, sustainable food sources.
Example: Impossible Foods & Beyond Meat use biotechnology to create plant-based meat substitutes with enhanced nutritional profiles.
5. Disease Detection & Early Warning Systems
- AI-powered crop disease detection systems prevent outbreaks.
- Genetic resistance engineering prevents viral crop diseases like rust and blight.
- Blockchain-based food traceability ensures food safety and transparency.
Example: AI-powered satellite imaging detects fungal outbreaks before they spread, saving entire harvests.
6. Vertical & Smart Farming Innovations
- Hydroponic & aeroponic systems maximize food production in urban areas.
- AI-managed greenhouses optimize temperature, humidity, and lighting.
- Automated robotic farming reduces labor costs and increases efficiency.
Example: Vertical farms in urban centers grow food year-round with 90% less water than traditional agriculture.
Benefits of Biotechnology in Agriculture
1. Increased Crop Yield & Food Security
Biotech innovations help feed growing populations by optimizing crop production and reducing losses.
2. Reduced Chemical Usage & Environmental Impact
Biotech reduces reliance on pesticides, herbicides, and synthetic fertilizers, promoting eco-friendly agriculture.
3. Climate Resilience & Sustainability
Genetically engineered crops withstand droughts, floods, and extreme weather conditions, ensuring stable food supplies.
4. Improved Nutritional Value & Food Quality
CRISPR and GMOs enhance protein, vitamins, and micronutrients in staple foods, improving global nutrition.
5. Precision Farming & Reduced Waste
AI-powered data analytics minimizes water, fertilizer, and resource waste, making agriculture more efficient and cost-effective.
Challenges in Agricultural Biotechnology
1. Public Perception & GMO Controversies
- Concerns about GMO safety and long-term health impacts remain.
- Misinformation affects consumer trust in biotech-enhanced food.
2. Regulatory & Ethical Concerns
- Governments enforce strict regulations on genetic modification.
- Ethical concerns about gene editing and biodiversity loss require ongoing discussion.
3. High Implementation Costs
- Biotech innovations require investment in R&D, infrastructure, and training.
- Small farmers struggle to access expensive biotech solutions.
4. Cybersecurity Risks in Precision Agriculture
- AI-driven farms and IoT systems are vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Blockchain and AI-based security solutions are needed to protect data integrity.
Future Trends in Agricultural Biotechnology (2025 & Beyond)
1. AI & Robotics in Smart Farming
- AI-driven autonomous tractors, drones, and robotic harvesters increase efficiency.
- Machine learning models optimize planting, irrigation, and harvesting schedules.
2. CRISPR Advancements for Super Crops
- Future CRISPR applications could eliminate allergens in food.
- Climate-proof crops resistant to extreme conditions will see broader adoption.
3. Blockchain & IoT for Food Traceability
- Blockchain ensures transparency in food supply chains.
- Smart sensors track farm-to-table food quality and prevent contamination.
4. Expansion of Cellular Agriculture & Lab-Grown Proteins
- Cultivated seafood, dairy, and poultry will gain mainstream acceptance.
- Governments will invest in alternative protein research to meet food demand.
5. Sustainable Water & Carbon Farming
- AI-driven irrigation will minimize water waste.
- Carbon sequestration in farming will combat climate change.
Conclusion
Biotechnology in agriculture is revolutionizing food production, sustainability, and global food security. As AI, CRISPR, and precision farming continue to advance, farmers and food producers will benefit from increased efficiency, higher yields, and environmentally-friendly practices.
What’s Next?
Are you ready for the biotech revolution in agriculture? Stay updated on gene editing, precision farming, and sustainable food innovations.
Share your thoughts! How do you see biotechnology shaping the future of agriculture? Let us know in the comments below!
7. Autonomous Vehicles
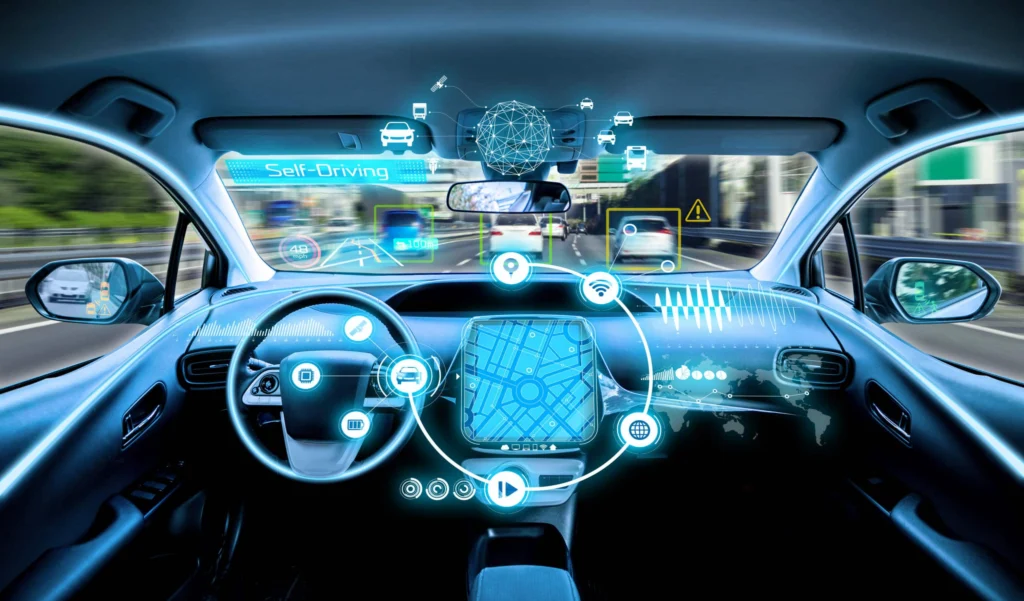

The Future of Autonomous Vehicles in 2025: Transforming Transportation and Mobility
Introduction
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are revolutionizing the transportation industry in 2025, offering enhanced safety, efficiency, and sustainability. With advancements in AI, 5G, and edge computing, self-driving technology is becoming more reliable and widespread. This blog explores the key applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends shaping the evolution of autonomous vehicles.
What Are Autonomous Vehicles?
Autonomous vehicles are self-driving cars, trucks, and public transit systems that use AI, sensors, and real-time data processing to navigate roads without human intervention.
Key Technologies Powering AVs:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Machine learning for decision-making and object recognition.
- Lidar & Radar Sensors: Real-time mapping and obstacle detection.
- 5G & V2X Communication: Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) data exchange.
- Edge Computing: Reducing latency for faster responses and improved safety.
Key Applications of Autonomous Vehicles in 2025
1. Self-Driving Cars & Ride-Sharing
- AI-powered ride-hailing services reduce congestion and improve accessibility.
- Fully autonomous taxi fleets (robotaxis) enhance urban mobility.
- Personalized AI-driven navigation systems for optimized route planning.
Example: Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Cruise are expanding their autonomous taxi networks.
2. Autonomous Trucks & Logistics
- Self-driving freight trucks streamline supply chains.
- AI-powered fleet management systems optimize fuel consumption.
- Automated last-mile delivery vehicles reduce operational costs.
Example: Amazon, UPS, and Daimler are investing in AV logistics to improve delivery efficiency.
3. Public Transport & Smart Cities
- AI-driven autonomous buses and shuttles improve urban mobility.
- Self-driving metro trains reduce energy consumption and enhance safety.
- 5G-powered smart intersections enable AV traffic coordination.
Example: Dubai and Singapore have deployed autonomous shuttles for public transportation.
4. Agriculture & Industrial Automation
- Self-driving tractors and harvesters enhance precision farming.
- AI-controlled logistics improve factory-to-market supply chains.
- Autonomous mining vehicles increase worker safety and efficiency.
Example: John Deere and Caterpillar use AVs for efficient, sustainable farming and mining operations.
5. Emergency & Law Enforcement Vehicles
- AI-driven ambulances reduce response times.
- Autonomous police vehicles enhance patrolling and crime prevention.
- AI-powered fire trucks optimize emergency route planning.
Example: Cities like Los Angeles and Tokyo are testing AV emergency fleets.
Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
1. Enhanced Safety & Accident Reduction
- AI-driven AVs eliminate human errors, reducing road accidents.
- Advanced sensor systems prevent collisions in real time.
2. Reduced Traffic Congestion
- AI-powered navigation improves traffic flow and reduces gridlocks.
- Vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication optimizes traffic lights and lanes.
3. Lower Carbon Emissions & Sustainability
- AVs improve fuel efficiency and adopt electric vehicle (EV) technology.
- AI-optimized route planning minimizes unnecessary fuel consumption.
4. Increased Accessibility & Mobility
- AVs provide mobility solutions for elderly and disabled individuals.
- Self-driving taxis enhance urban and rural connectivity.
5. Cost Savings for Businesses & Consumers
- Lower insurance premiums due to reduced accident risks.
- Fleet automation reduces labor costs for logistics and ride-sharing services.
Challenges in Autonomous Vehicle Adoption
1. Regulatory & Legal Barriers
- Governments require extensive safety testing and approvals.
- Insurance policies must adapt to autonomous vehicle liability concerns.
2. Cybersecurity Risks & Data Privacy
- Hacking threats on AV networks require robust cybersecurity measures.
- Data privacy concerns arise from continuous AV monitoring and tracking.
3. High Development & Infrastructure Costs
- AV R&D is expensive, with substantial investments needed for sensors, AI, and connectivity.
- Smart road infrastructure upgrades are required for seamless AV operation.
4. Public Trust & Adoption Resistance
- Consumers have concerns over safety, reliability, and control.
- Governments and companies must educate the public on AV benefits and security.
Future Trends in Autonomous Vehicles (2025 & Beyond)
1. AI-Enhanced Autonomous Driving
- Neural networks will enable real-time learning and decision-making.
- AI-driven predictive analytics improve route planning and hazard detection.
2. Fully Autonomous Public Transport
- Major cities will expand self-driving bus and metro networks.
- Governments will invest in smart road infrastructure and AV-friendly policies.
3. Expansion of Autonomous Delivery Services
- Drone deliveries and AV-powered last-mile logistics will become mainstream.
- AI-powered autonomous grocery deliveries will enhance e-commerce efficiency.
4. Integration of 6G & Smart Cities
- 6G networks will further enhance real-time AV communication.
- Smart highways with embedded sensors will enable seamless AV navigation.
5. Ethical AI & Decision-Making Regulations
- Governments will define moral guidelines for AV accident scenarios.
- AI ethics committees will ensure fair decision-making in autonomous driving.
Conclusion
Autonomous vehicles in 2025 are reshaping transportation, logistics, and urban mobility, driving advancements in safety, efficiency, and sustainability. As AI, 5G, and edge computing continue to evolve, AVs will redefine how we move and interact with smart cities.
What’s Next?
Are you ready for the autonomous vehicle revolution? Stay updated on self-driving innovations, AV regulations, and smart mobility trends.
Share your thoughts! How do you see autonomous vehicles shaping the future of transportation? Let us know in the comments below!
8. Blockchain

The Future of Blockchain Technology in 2025: Revolutionizing Security, Finance, and Beyond
Introduction
Blockchain technology in 2025 continues to disrupt multiple industries, providing enhanced security, transparency, and decentralization. With innovations in Web3, smart contracts, and decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain is transforming finance, supply chains, healthcare, and data security. This blog explores the key applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends shaping blockchain’s evolution.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions securely and transparently across multiple nodes.
Key Features of Blockchain:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network.
- Transparency: Public ledgers allow for auditability.
- Immutability: Transactions are tamper-proof once recorded.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts automate transactions.
Key Applications of Blockchain in 2025
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) & Cryptocurrencies
- Blockchain-powered lending, borrowing, and trading platforms.
- Stablecoins and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) reshape global payments.
- AI-driven smart contract automation enhances DeFi efficiency.
Example: Ethereum 2.0’s transition to proof-of-stake (PoS) improves transaction scalability and security.
2. Supply Chain Transparency & Logistics
- Blockchain-enabled tracking systems provide real-time data on goods.
- Smart contracts ensure contract compliance and fraud prevention.
- AI-integrated blockchain predicts demand and optimizes logistics.
Example: Walmart and IBM use blockchain for real-time food safety tracking.
3. Healthcare & Medical Data Security
- Blockchain secures patient records and prevents data breaches.
- AI-driven health data analysis enhances predictive healthcare.
- Decentralized identity verification improves patient consent management.
Example: Hospitals integrate blockchain-powered patient health records for seamless cross-hospital access.
4. Digital Identity & Cybersecurity
- Blockchain prevents identity theft and fraud with self-sovereign identities.
- Decentralized authentication replaces traditional password-based systems.
- AI-powered fraud detection improves online security.
Example: Governments issue blockchain-based digital IDs to enhance cybersecurity and citizen authentication.
5. NFTs & the Creator Economy
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) empower artists and content creators.
- Smart contracts automate royalty payments for digital assets.
- AI-generated NFTs introduce programmable digital art.
Example: Platforms like OpenSea and Rarible expand NFT marketplaces for gaming, music, and virtual assets.
6. Blockchain in Governance & Voting Systems
- Secure, transparent e-voting systems eliminate election fraud.
- Blockchain ensures tamper-proof public records and land registries.
- AI-powered fraud prevention mechanisms strengthen democratic processes.
Example: Governments explore blockchain-based e-voting to increase election integrity.
7. Green Blockchain & Sustainability Initiatives
- Energy-efficient PoS and carbon-negative blockchain networks emerge.
- AI-enhanced blockchain tracks carbon footprints and energy consumption.
- Decentralized renewable energy trading enables peer-to-peer transactions.
Example: Companies like Ethereum and Cardano prioritize eco-friendly blockchain solutions.
Benefits of Blockchain Expansion
1. Enhanced Security & Fraud Prevention
- Decentralization prevents data manipulation and unauthorized access.
- Immutable records make data tampering nearly impossible.
2. Cost Savings & Operational Efficiency
- Smart contracts reduce administrative costs in finance, insurance, and law.
- Blockchain eliminates intermediaries, reducing transaction fees.
3. Greater Transparency & Trust
- Public ledgers ensure verifiable, real-time transactions.
- Blockchain reduces corruption and enhances corporate accountability.
4. Global Financial Inclusion
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) enables banking access for unbanked populations.
- Cryptocurrency-based remittances reduce cross-border payment costs.
Challenges of Blockchain Adoption
1. Regulatory Uncertainty & Compliance Issues
- Global regulations for crypto and DeFi remain fragmented.
- Governments debate legal frameworks for smart contracts and digital assets.
2. Scalability & High Transaction Costs
- Legacy blockchain networks struggle with slow transaction speeds.
- Ethereum 2.0 and Layer-2 solutions address scalability issues.
3. Security Risks & Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
- Smart contracts are prone to coding errors and hacking attacks.
- DeFi platforms face frequent security breaches and rug pulls.
4. Public Perception & Adoption Barriers
- Misinformation and skepticism slow mainstream blockchain adoption.
- Education initiatives are needed to bridge the knowledge gap.
Future Trends in Blockchain (2025 & Beyond)
1. AI & Blockchain Integration
- AI-powered smart contracts optimize automation and security.
- Machine learning-driven fraud detection enhances DeFi safety.
2. Multi-Chain & Cross-Chain Interoperability
- Bridges between blockchain networks improve data transfer and scalability.
- Polkadot, Cosmos, and Chainlink enable seamless multi-chain transactions.
3. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) & Institutional Adoption
- Governments launch national digital currencies for regulated blockchain payments.
- Banks integrate blockchain for instant settlements and remittances.
4. Metaverse & Web3 Expansion
- Blockchain-powered virtual worlds enhance digital asset ownership.
- Decentralized apps (dApps) dominate Web3 infrastructure.
5. Sustainable & Energy-Efficient Blockchain Solutions
- Eco-friendly consensus mechanisms (PoS, Proof-of-Authority) replace PoW.
- Carbon-neutral blockchain initiatives reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology in 2025 is reshaping finance, security, supply chains, and digital governance. With continued advancements in DeFi, AI integration, and sustainability, blockchain’s potential is expanding beyond cryptocurrency.
What’s Next?
Are you ready for the blockchain revolution? Stay updated on smart contracts, Web3 innovations, and decentralized applications.
Share your thoughts! How do you see blockchain transforming industries? Let us know in the comments below!
9. Edge Computing

The Future of Edge Computing in 2025: Enhancing Speed, Security, and IoT Connectivity
Introduction
Edge computing is revolutionizing data processing in 2025, bringing low-latency, high-speed computation closer to users and devices. As the demand for real-time processing, AI-driven automation, and IoT connectivity grows, edge computing is transforming industries, smart cities, and cloud infrastructure. This blog explores the key applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends shaping edge computing.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing refers to processing data closer to the source (near IoT devices, sensors, or local servers) rather than relying solely on centralized cloud computing.
Key Features of Edge Computing:
- Low Latency: Faster data processing and response times.
- Reduced Bandwidth Usage: Localized data analysis minimizes cloud data transfer.
- Enhanced Security: Sensitive data processing at the edge reduces cyberattack risks.
- AI-Powered Automation: Real-time decision-making without cloud dependency.
Key Applications of Edge Computing in 2025
1. Internet of Things (IoT) & Smart Cities
- AI-powered traffic management optimizes real-time congestion control.
- Smart energy grids enhance sustainability and reduce power outages.
- Edge-enabled surveillance cameras improve security with real-time facial recognition.
Example: Cities like Singapore and Amsterdam leverage edge computing for smart infrastructure management.
2. Autonomous Vehicles & Transportation
- Edge processing in self-driving cars ensures real-time navigation and obstacle detection.
- Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication enhances road safety.
- AI-powered predictive maintenance reduces downtime for fleet operators.
Example: Tesla and Waymo use edge-based AI models for autonomous driving.
3. Healthcare & Remote Patient Monitoring
- Edge-powered wearable devices track patient vitals in real time.
- AI-driven remote diagnostics enable faster medical responses.
- Decentralized health data storage ensures patient privacy and compliance.
Example: Hospitals use edge-enabled IoT sensors for smart medical monitoring.
4. Industrial Automation & Smart Manufacturing
- Edge-driven robotics optimize factory automation.
- AI-powered predictive maintenance reduces operational costs.
- Real-time quality control monitoring enhances production efficiency.
Example: Siemens and General Electric integrate edge AI for smart factories.
5. Retail & E-Commerce Innovations
- AI-driven personalized shopping experiences enhance customer engagement.
- Edge-based checkout systems eliminate wait times.
- Supply chain optimization reduces delays and enhances delivery speed.
Example: Amazon uses edge computing for real-time inventory management.
6. Cybersecurity & Data Protection
- Decentralized data processing reduces cloud vulnerabilities.
- AI-driven threat detection prevents cyberattacks in real time.
- Secure IoT networks enhance privacy for connected devices.
Example: Enterprises deploy edge security frameworks for endpoint protection.
7. Gaming & Augmented Reality (AR) / Virtual Reality (VR)
- Edge-powered cloud gaming reduces latency for seamless gameplay.
- AI-enhanced AR/VR experiences optimize real-time rendering.
- 5G-enabled mobile gaming delivers ultra-responsive interactions.
Example: Microsoft’s Xbox Cloud Gaming leverages edge servers for real-time performance.
Benefits of Edge Computing
1. Faster Processing & Lower Latency
- Real-time data analysis reduces delays in critical applications.
- Ideal for autonomous vehicles, healthcare monitoring, and financial trading.
2. Enhanced Security & Privacy
- Localized data processing minimizes data exposure to cyber threats.
- Compliance with strict privacy regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA).
3. Cost Savings & Efficient Bandwidth Usage
- Reduces cloud storage and network congestion costs.
- AI-driven workload distribution optimizes infrastructure investments.
4. Scalability & AI-Driven Automation
- Enables hyper-local decision-making in IoT ecosystems.
- Edge AI models continuously improve efficiency and accuracy.
Challenges in Edge Computing Adoption
1. Infrastructure Deployment & Maintenance
- Requires distributed computing resources across multiple locations.
- Upgrading legacy systems involves high initial investment.
2. Data Security & Compliance Concerns
- Protecting decentralized edge nodes from cyberattacks.
- Ensuring real-time security patches for edge devices.
3. Interoperability & Standardization Issues
- Various edge frameworks lack universal compatibility.
- Businesses require integrated multi-cloud and edge solutions.
4. AI Model Training & Performance Optimization
- AI-driven edge applications need continuous learning updates.
- Balancing energy efficiency and high-performance computation.
Future Trends in Edge Computing (2025 & Beyond)
1. AI-Powered Edge Networks
- AI-driven workload balancing optimizes resource allocation.
- Predictive AI models enhance autonomous decision-making.
2. 5G & Edge Computing Synergy
- Ultra-fast 5G networks reduce edge computing latency.
- AI-driven network slicing prioritizes critical applications.
3. Blockchain & Secure Edge Networks
- Decentralized edge ledgers ensure tamper-proof data transactions.
- Blockchain-powered IoT identity authentication enhances security.
4. Edge-Powered AR/VR & Metaverse Development
- AI-driven real-time rendering improves VR experiences.
- 5G-enabled metaverse applications leverage edge servers.
5. Sustainable & Energy-Efficient Edge Solutions
- Low-power AI chips optimize processing efficiency.
- Green edge computing infrastructure reduces carbon footprints.
Conclusion
Edge computing in 2025 is revolutionizing real-time data processing, AI-driven automation, and IoT connectivity. With advancements in 5G, cybersecurity, and AI, businesses and smart cities are adopting edge-powered solutions to drive innovation.
What’s Next?
Are you ready to explore the next evolution of edge computing? Stay updated on AI-driven edge innovations, secure computing trends, and future digital transformations.
Share your thoughts! How do you see edge computing shaping industries? Let us know in the comments below!
10. Personalized Medicine
The Future of Personalized Medicine in 2025: Revolutionizing Healthcare with Precision Treatments
Introduction
Personalized medicine in 2025 is transforming healthcare by offering customized treatments based on an individual’s genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. With advancements in genomics, AI-driven diagnostics, and precision drug development, personalized medicine is leading to better patient outcomes, reduced side effects, and optimized therapies. This blog explores key applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends shaping personalized medicine.
What is Personalized Medicine?
Personalized medicine, also known as precision medicine, involves tailoring medical treatments to an individual’s unique genetic makeup, medical history, and lifestyle.
Key Technologies Driving Personalized Medicine:
- Genomics & DNA Sequencing: Unlocks genetic insights for targeted therapies.
- AI & Machine Learning: Analyzes big data to predict treatment responses.
- CRISPR & Gene Editing: Modifies genes to correct genetic disorders.
- Wearable Health Tech: Provides real-time patient monitoring and analytics.
- Bioinformatics: Integrates multi-omics data for precise medical decisions.
Key Applications of Personalized Medicine in 2025
1. Genomics & Targeted Therapy
- AI-driven genetic analysis identifies disease risks and drug responses.
- Personalized cancer treatments based on genetic mutations.
- Gene therapy advancements correct inherited genetic disorders.
Example: Companies like 23andMe and Illumina provide genetic testing for disease predisposition and treatment plans.
2. AI-Powered Diagnostics & Predictive Medicine
- AI-driven early disease detection and biomarker analysis.
- Machine learning models predict individual responses to treatments.
- Real-time data from wearables and smart health devices enhance diagnostics.
Example: IBM Watson Health uses AI to provide personalized treatment recommendations.
3. Pharmacogenomics & Precision Drug Development
- Customized drug prescriptions based on genetic compatibility.
- Reduced adverse drug reactions by analyzing genetic responses.
- AI-accelerated drug discovery and testing.
Example: The FDA-approved AI-driven drug discovery platforms shorten pharmaceutical research timelines.
4. Personalized Cancer Treatments
- Immunotherapy tailored to a patient’s tumor profile.
- AI-powered liquid biopsies for non-invasive cancer detection.
- CRISPR-driven gene editing solutions for cancer therapy.
Example: Companies like Caris Life Sciences use genomic profiling for personalized oncology treatments.
5. Wearable Health Devices & Remote Monitoring
- Continuous glucose monitoring for diabetics.
- AI-driven heart rate and oxygen saturation tracking.
- Smartwatches detecting irregular heart rhythms and early stroke signs.
Example: Apple and Fitbit integrate AI-based predictive health analytics into their wearables.
6. AI in Personalized Nutrition & Wellness
- AI-powered diet plans based on microbiome and DNA analysis.
- Personalized vitamin and supplement recommendations.
- Predictive models for weight loss and metabolic disorders.
Example: Viome and Nutrigenomix provide personalized diet plans based on gut microbiome and genetic analysis.
Benefits of Personalized Medicine
1. More Effective Treatments & Better Outcomes
- Genetically tailored therapies improve efficacy compared to one-size-fits-all treatments.
- AI-driven insights predict treatment success rates.
2. Reduced Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
- Pharmacogenomics prevents adverse drug reactions.
- Precision oncology minimizes chemotherapy toxicity.
3. Early Disease Detection & Prevention
- AI-driven biomarkers detect diseases before symptoms appear.
- Personalized risk assessments enable proactive healthcare.
4. Cost Savings & Healthcare Efficiency
- Preventative treatments reduce hospitalization costs.
- AI-powered drug discovery lowers pharmaceutical R&D expenses.
Challenges in Personalized Medicine
1. High Costs & Accessibility Issues
- Genetic testing and precision therapies remain expensive.
- Insurance companies struggle with coverage policies for personalized treatments.
2. Data Privacy & Ethical Concerns
- Secure handling of genetic and biometric data is crucial.
- Ethical concerns over genetic modifications and patient consent.
3. Integration with Traditional Healthcare
- Healthcare providers need training to adopt AI and genomics.
- Electronic health record (EHR) systems must support precision medicine data.
4. Regulatory Challenges & FDA Approvals
- Strict regulations slow down genetic therapy approvals.
- AI-driven drug discovery faces compliance hurdles in clinical trials.
Future Trends in Personalized Medicine (2025 & Beyond)
1. AI & Big Data-Driven Drug Development
- AI accelerates drug discovery and clinical trial predictions.
- Digital twin models simulate patient responses to new drugs.
2. Expansion of Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing
- Home genetic testing kits enable early disease detection.
- AI-driven telemedicine platforms integrate genetic risk assessments.
3. CRISPR & Gene Editing Advancements
- Next-gen CRISPR techniques enable precise gene corrections.
- Personalized gene therapy expands to rare genetic disorders.
4. AI-Powered Virtual Health Assistants
- AI chatbots provide real-time personalized medical advice.
- Wearable AI assistants analyze health trends and recommend actions.
5. Blockchain for Secure Health Data Management
- Decentralized health records enhance patient privacy and security.
- AI-integrated blockchain protects genomic and biometric data.
Conclusion
Personalized medicine in 2025 is revolutionizing healthcare, offering precision treatments, early disease detection, and AI-powered diagnostics. As AI, genomics, and wearable technology advance, patients will benefit from highly tailored, efficient, and accessible medical solutions.
What’s Next?
Are you ready for the personalized medicine revolution? Stay informed about genomic innovations, AI-driven treatments, and precision healthcare advancements.








